Endocannabinoid System
A system of specialized receptors is found in the brain and peripheral nervous system throughout the body of all vertebrates and mammals. It is found in primitive animals 600 million years ago and every animal except insects. Recent research indicates that the Endocannabinoid System (ES) appears to play a “protective” role in our bodies. In fact, the most important thing the ES wants to protect is homeostasis – that is, making sure that the body is functioning optimally at all times. Due to the success stories of the medicinal use of hemp products, the ES is now being discussed during the medical training of US physicians.
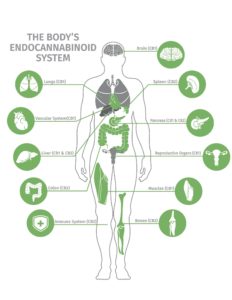
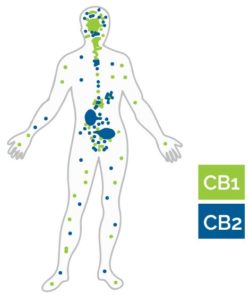
In the late 1980s, scientists discovered these cannabinoid receptors and named them CB1, which was most abundant in the brain and central nervous system and CB2, as opposed to CB1, was found mostly in the peripheral cells, especially in the immune system. CB1 receptors are also found in the lungs, bloodvessels, muscles, digestive tract, and reproductive organs. The stimulation of CB1 receptors has psychoactive and behavioral effects. CB2 receptors are primarily found in the liver, bone marrow, pancreas, and brain stem. CB2 receptors are involved in the modulation of a number of biological functions, including inflammation and pain response.
Humans naturally produce endogenous cannabinoids (endocannabinoids) to bind to these receptors called anandamide and 2-archidonoylglyverol (2-AG). These endocannabinoids are released from the nerve cells to back regulate the nerve activating neurotransmitter. Thus, endocannabinoids modulate every other neurotransmitter in an effort to maintain the body’s homeostasis (balance).
The plant chemicals found in cannabis (phytocannabinoids) closely mimics the body’s endogenous cannabinoids to bind to the same receptor system. The phytocannabinoids occur naturally within the cannabis sativa plant and include over eighty or more chemicals including omega fatty acids that interact with the cannabinoid receptors. These include the two well-known cannabinoids, Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). THC mimics the natural endocannabinoid, anandamide, to stimulate CB1 receptors to produce psychiatric and circulatory effects. CBD lacks the psychoactive effects of THC and appears to have many health benefits.
Endocannabinoid Deficiency Syndrome
Unfortunately, modern US diets do not always contain the nutrition required to maintain the endocannabinoid system properly. In cases where nutritional deficiencies or other problems are causing the endocannabinoid system to fail, a person may develop a condition known as “Endocannabinoid Deficiency Syndrome”. This can lead to a variety of symptoms and related conditions, including irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, migraines and more.
If your diet doesn’t contain a sufficient amount of Omega-3 fatty acids, your body may be unable to produce the proper amount of endogenous cannabinoids on its own. In addition, because Omega-3 fatty acids grow and repair your CB1 receptors, the cannabinoids your body does produce may not affect the endocannabinoid system as strongly as they should.